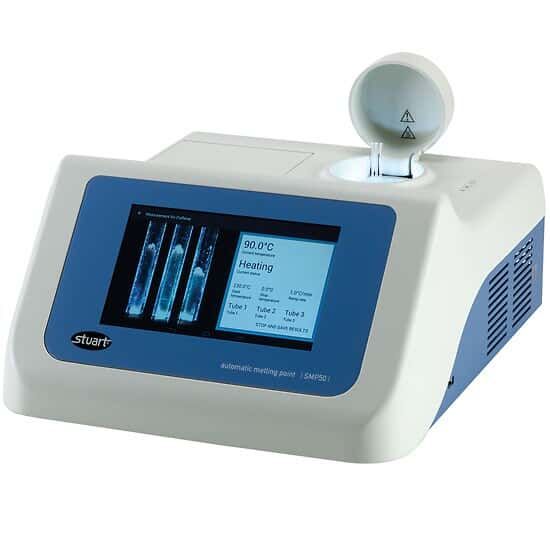
Melting Point Apparatus

A melting point apparatus is a laboratory instrument used to determine the melting point of a substance with high accuracy. The melting point is the temperature at which a solid change into a liquid, and it serves as an important parameter for identifying and characterizing chemical compounds, checking purity, and quality control in laboratories. The apparatus generally consists of a heating unit, a temperature control system, a capillary sample holder, and an observation system (microscope or magnifying lens). It is widely used in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, research laboratories, and educational institutions for analysing organic and inorganic compounds.
Properties of Melting Point Apparatus
- Accurate Temperature Measurement – Provides precise determination of melting points with digital or analog temperature readouts.
- Heating System – Equipped with a uniform heating source (electric heater or oil bath).
- Sample Holder – Uses capillary tubes or glass tubes for holding solid samples.
- Observation Facility – May include magnifying lens, digital display, or camera for monitoring phase changes.
- Digital Models – Some advanced versions feature programmable temperature ramping and automatic detection.
- Temperature Range – Usually covers a broad range (room temperature up to 300–400°C, depending on the model).
- User-Friendly Design – Compact, easy to operate, and suitable for routine laboratory testing.
- Safety Features – Overheat protection and insulated casing for safe operation.
- Applications – Used in research, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and academic labs for compound characterization and purity analysis.